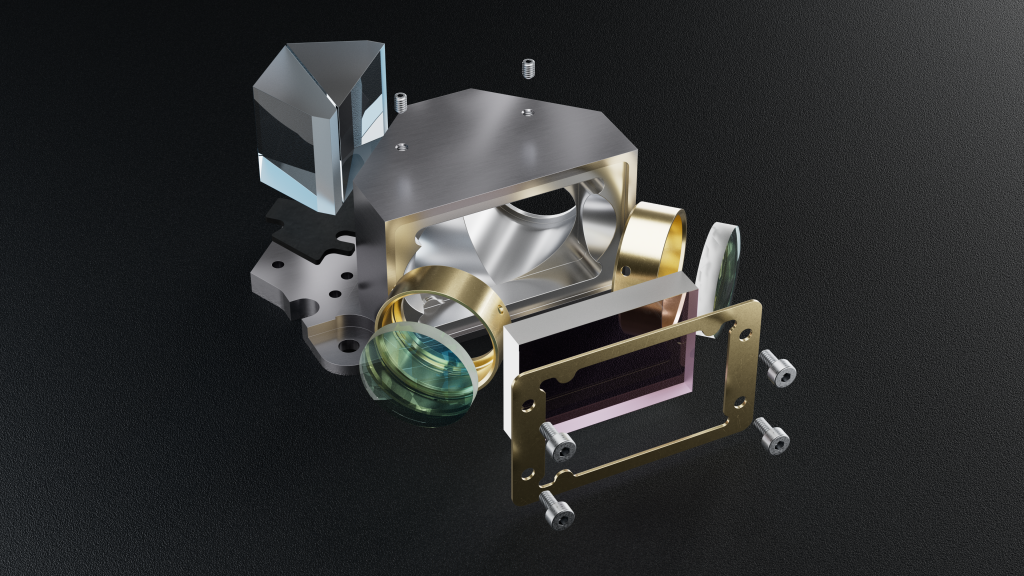
Optomechanical Assembling
Altechna offers a full range of assembly and manufacturing solutions, from exact build-to-print projects based on customer’s instructions, to fully custom-designed solutions that are tailored to fit the specific end-user needs:
- Optical parts: prisms, waveplates, lenses, and other glass parts optically contacted or cemented together.
- Optomechanical parts: optics mounted on various types of metal mounts and housings, either fixed or shifting.
Optomechanical solutions are designed and manufactured in-house to fit your specific needs. From exact build-to-print projects – to fully custom-designed solutions. We’ve got you covered!
Type of work offered
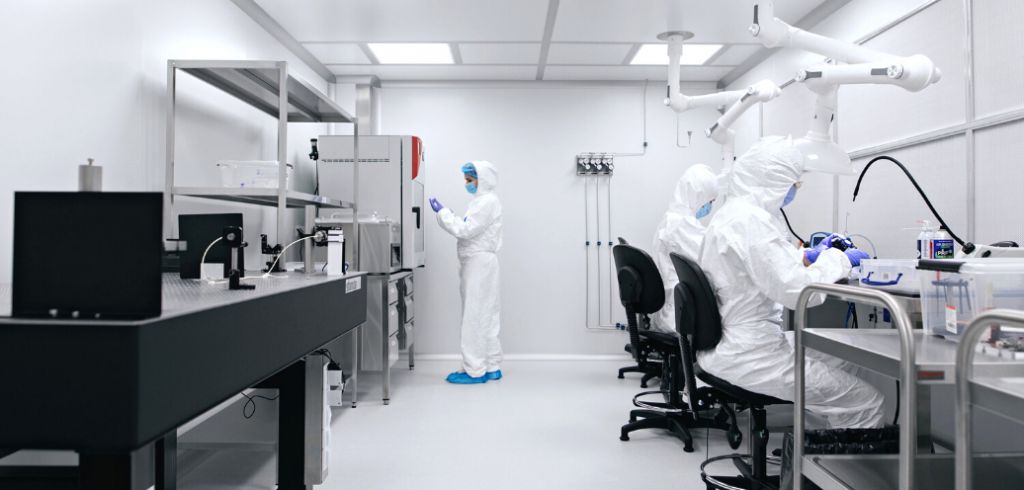
We offer a variety of assembly and manufacturing solutions in ISO 6 cleanroom environment. Starting with exact build-to-print projects based on customer instructions, and ending with fully custom-designed solutions, these are tailored to fit the specific end-user needs.
Any work is accompanied by:
- Rapid reviews of project needs by a dedicated engineering team
- A design-to-cost mentality
- A clear information flow, strict deadlines, and full customer involvement
- Quality control pre- and post-manufacturing, all carried out in-house
- Full traceability of each manufacturing stage
Our goal is to provide a service whereby we can help the end-user to gain the following additional benefits:
- Time and resource savings: the complex, multi-stage processes required to build optomechanical sub-assemblies demand a large amount of internal resources and time.
- Simplicity: the pre-built, aligned, and cleanroom-packed modules can immediately be incorporated into the users’ systems.
- Increased yield: reducing customer headaches from damages to precision optics when being built into assemblies.
- Space-saving: with goods coming from Altechna, a company‘s own cleanroom areas and manufacturing lines can be reallocated to other projects.
- Cost saving: a skilled team of technical experts is ready to help with your needs for the most competitive price on the market.
Benefits
Pre-built and modules ready to be incorporated into the system
Continuous post-manufacturing technical support
Altechna’s strategic partners provide necessary metal and plastic parts, as well as other components. We ensure quality and repeatability.
Coating types
Available Coating Technologies
Magnetron Sputtering
Magnetron Sputtering (Bühler Helios 800 coater) ensures precise control of very thin layers at atomic scale, bringing you top grade products and high yield.
Capacity
- 1300 pcs. of Ø12.7 mm
- 340 pcs. of Ø25.4 mm
- 80 pcs. of Ø50.8 mm
- 40 pcs. of Ø76.2 mm
- 10 pcs. of Ø101.6 mm
- 10 pcs. of Ø200 mm
Cutting Edge Coatings NAVIGATOR 700
Ion Beam Sputtering
Ion Beam Sputtering (Cutting Edge Coatings NAVIGATOR 700 coater) is the best option when extreme process control is required to achieve the highest lossless spectral performance possible in small volumes.
Performance
- Minimum reflectance <0.1%
- Maximum reflectance >99.99%
- Extinction ratio 1:1000
- Absorption <1 ppm
- LIDT:
- >30 MW/cm2 @1070 nm, CW
- >95 J/cm2 @1064 nm, 10 ns
- >1.5 J/cm2 @1030 nm, 500 fs
Capacity
- 53 pcs. of Ø25.4 mm
- 11 pcs. of Ø50.8 mm
- 6 pcs. of Ø 76.2 – 101.6 mm
- 3 pcs. of Ø101.6 mm
- 1 pcs. of Ø150 mm
- Coating and mechanical solutions for custom-shaped substrates possible.
Materials
- Al2O3, HfO2, Nb2O5, SiO2, Ta2O5, TiO2
- Materials mixture
Ion Assisted E-Beam
Ion assisted electron beam evaporation (Bühler SyrusPro 1350 coater) is an excellent solution for mass production which produces excellent coatings at extremely competitive deposition rates for a broad range of applications and wavelengths.
Performance
- Minimum reflectance <0.1%
- Maximum reflectance >99.9%
- Extinction ratio 1:1000
Capacity
- 652 pcs. of Ø25.4 mm
- 160 pcs. of Ø50.8 mm
- 76 pcs. of Ø76.2 mm
- 36 pcs. of Ø101.6 mm
- 4 pcs. of Ø200 mm
- 4 pcs. of Ø300 mm
- Coating and mechanical solutions for custom-shaped substrates available.
Materials
- HfO2, Nb2O5, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, SiO2
- MgF2, LaF3 (without IAD)
Technology Comparison
|
Magnetron Sputtering |
Ion Beam Sputtering |
Ion Assisted E-Beam |
| Spectral ranges |
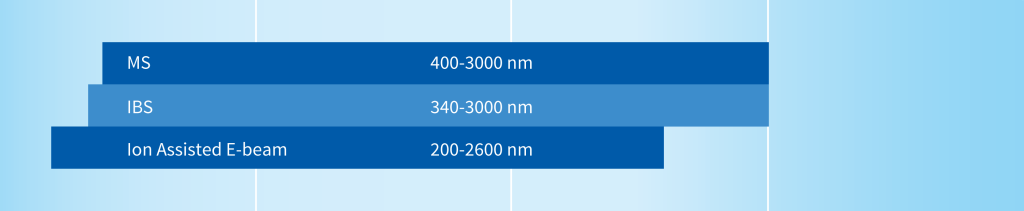
400-3000 nm |
340-3000 nm |
200-2600 nm |
| Capacity 1"* |
370 |
53 |
652
|
| Density |
Near bulk |
Near bulk |
Very dense |
| Aging effects |
No |
No |
No |
| Environmental resistance |
High |
High |
Mid |
| Maximum reflectivity |
>99.99% |
>99.99% |
>99.9% |
| Minimum reflectivity |
<0.1% |
<0.1% |
<0.1% |
| Extinction ratio |
1:1000 |
1:1000 |
1:1000 |
| Price** |
●● |
●●● |
● |
* Maximum capacity varies depending on required spectral specifications.
** On a scale from 1 to 3. Number “1” marks the price as low.
Spectral Range
ISO 6 Cleanroom Working areas
In recent years, Altechna has strengthened by investing in the areas of manufacturing, including a newly built cleanroom area, equipment, as well as technical training for our team members.
Currently, our facilities include:
- 100 m2 ISO 6 cleanroom working area.
- All the necessary equipment for optomechanical assembly work.
- A choice of various acrylic-based and epoxy adhesives.
- Custom measurement-system set-ups based on the final application.
- Experienced team of engineers and assemblers.
One Source
Altechna is your single source for all photonics solutions, reducing your supplier count to one.
Established quality gates:
- After each manufacturing phase, all raw materials, sub-assemblies, sub-components, and parts are reviewed by the established quality gates.
- The final optomechanical products leaving Altechna are of superior quality, pre-aligned, tested and certified in ISO 6 work areas.
- This leads to a reduction of your productʼs time-to-market to the bare minimum, and it is done with market-leading speed and quality that is second to none.
Experienced Team
With dedicated engineering, quality control, and manufacturing teams, we achieve the lowest possible product-return rate.
This is guaranteed by:
- Excellent tooling design, assembly processes, and quality control all carried out in-house by experienced teams.
- Experience working with a wide variety of metal, glass, and plastic materials.
- Strong emphasis on customer support to identify critical aspects of projects.
Our goal is to provide a single source service for all photonics solutions. One source for all your optomechanical projects. Staring with the design, procurement of all necessary parts and ending with a final product.